Light Gauge Steel for Green Roof and Façade Systems
Pioneering sustainable design with robust light gauge steel, seamlessly integrating verdant green roofs and innovative façade systems to forge resilient, beautiful, and eco-conscious architectural marvels.

The Future of Sustainable Building Design
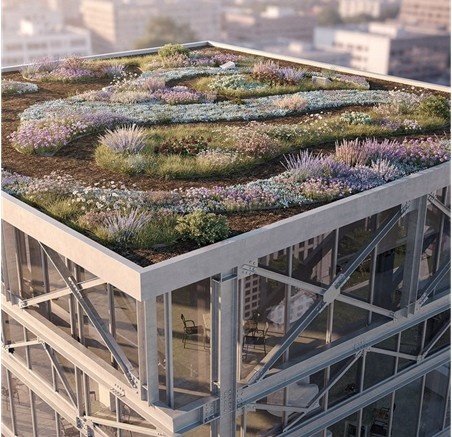
The construction industry is experiencing a fundamental shift toward environmentally conscious design. Green roofs and living façades have emerged as powerful solutions, offering thermal regulation, stormwater management, and enhanced urban biodiversity.
But behind every successful green installation lies a critical structural decision: the supporting framework. Light gauge steel has become the material of choice for architects and engineers seeking to balance sustainability goals with structural performance. Its unique properties make it ideal for supporting vegetative systems while contributing to overall building efficiency and longevity.
Light gauge steel refers to cold-formed steel members with thicknesses typically ranging from 0.0147 to 0.1017 inches. Unlike hot-rolled structural steel, these components are shaped at room temperature, creating precise, uniform profiles that integrate seamlessly with modern construction methods.
Delivers exceptional load-bearing capacity without adding significant structural burden to the building.
Maintains precise measurements regardless of moisture exposure, critical for vegetative systems.
Computer-controlled manufacturing ensures consistent quality and tight tolerances for faster installation.
When properly coated and detailed, light gauge steel systems can last 50+ years, often outliving the vegetative components they support. This durability makes them a smart investment for developers and facility managers planning long-term building performance.
Understanding Light Gauge Steel in Green Applications
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Dimensional Stability
Factory Precision
Sustainability Advantages That Matter
For project teams pursuing LEED certification or ESG goals, light gauge steel offers compelling environmental credentials. The material consists of up to 90% recycled content and remains 100% recyclable at end-of-life, creating a truly circular material flow.
Manufacturing processes have evolved significantly, with modern mills using electric arc furnaces that reduce energy consumption by 75% compared to traditional steelmaking. The lightweight nature of the material also translates to reduced transportation emissions during delivery to job sites.
Perhaps most importantly, precision fabrication minimizes on-site waste. Components arrive cut to exact specifications, reducing material waste by up to 20% compared to field-cut alternatives.
Structural Performance for Green Roof Systems
Green roofs present unique structural challenges. Saturated growing media can weigh 15-50 pounds per square foot, depending on depth and water retention. Add plant material, maintenance equipment access, and potential snow loads, and the engineering becomes complex quickly.
Light gauge steel framing excels in these applications through several mechanisms. The material's high strength allows for longer spans between supports, reducing the number of penetrations through waterproofing membranes. Its corrosion-resistant coatings—typically galvanized or galvalume finishes—withstand constant moisture exposure without degradation.
Key Structural Considerations
-
For extensive green roofs with shallow growing media, light gauge steel purlins and joists efficiently transfer loads to primary structural members. Intensive systems with deeper soil profiles may incorporate heavier cold-formed sections or hybrid systems combining light gauge components with conventional steel.
-
Load calculations must account for saturated soil weight
-
Thermal expansion joints prevent stress accumulation
-
Slope requirements ensure proper drainage
-
Access provisions for maintenance equipment
-
Integration with roof edge and fall protection systems
Establish primary steel framework anchored to building structure with appropriate standoff distance for drainage and air circulation.
Attach secondary framing members to accommodate specific planting tray or panel systems selected by landscape architect.
Coordinate pathways for irrigation lines, drainage systems, and electrical connections for lighting or monitoring equipment.
Façade Applications and Design Flexibility
Subframe Design
Module Integration
Service Routing
Engineering teams working with companies like Consac leverage BIM workflows to coordinate steel framing with waterproofing transitions, drainage components, and building envelope details. This digital approach identifies conflicts before fabrication, reducing costly field modifications.
Connection details deserve particular attention. Fasteners must penetrate only designated attachment zones within the roof assembly, maintaining waterproofing integrity. Thermal breaks may be required where steel members bridge insulation layers to prevent condensation. Expansion provisions accommodate seasonal movement without stressing connections.
Coating selection impacts long-term performance significantly. Galvanized finishes (G90 minimum) suit most applications, while coastal or industrial environments may warrant heavier coatings or stainless steel for critical components exposed to runoff from growing media.
Design and Detailing Best Practices
Load Analysis & Material Spec
Connection Detailing & Waterproofing Coordination
Coating Selection & Quality Assurance
What's Your Reaction?